Definition of Credit Rating
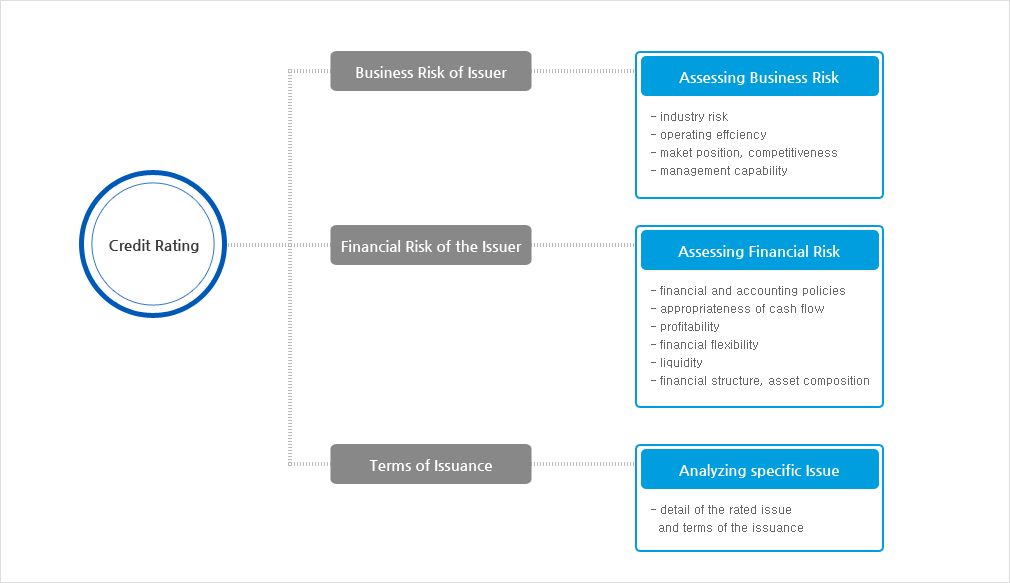
Rating Factors
Issuer Rating, Bond Rating, CP Rating, IFS Rating
Bond rating is the process where analysts systematically assess how probable it is that a specific issue will make timely principal and interest payment and then materialize the assessment results into a credit rating. They determine the probability of timely payment based on both external factors and internal ones such as the issuer’s capability and protection measures to deal with any changes within the company.
Risks that affect an issuer’s repayment capability and its stability are divided into two categories: business risk and financial risk. Therefore, credit assessment considers not just financial elements and prospect of the rated issuer but also the overall picture When assigning a CP ratingof the issuer’s industry, businesses it is engaged in and management status.
Factors considered in bond rating are also explored in insurer financial strength rating. However, rather than assessing ability to fufill financial obligation and probability of timely principal and interest repayment, the rating system is designed to evaluate the insurer’s overall financial strength and ability to meet its policyholder obligations.
ABS
ABS ratings review various risk factors and risk management methods through detailed analysis based on cash flow and asset quality of securities. By assessing the required level of credit enhancement through analyzing cash flow that reflects stress scenario, the rating system is designed to evaluate the probability of timely repayment of principal and interest on asset-backed securities.
In ABS ratings, credit quality of underlying assets, credit enhancement, legal risk, and credit quality and service capability of deal participants are evaluated.
Credit quality of the underlying assets : historical delinquency, loss ratio, collection rate and policy, etc.
Credit enhancement : subordination ratio, credit line, reserve account, etc.
Legal stability of the deal structure : true sale of the assets, perfection of security interest, bankruptcy remoteness of the issuer, bankruptcy remoteness of other securitization participants, commingling risk, etc.